Home »
Geology Tutorial
Sections of Engineering Geology
Learn about the Sections of Engineering Geology.
Submitted by Devyani Nagare, on March 10, 2022
Engineering geology includes the application of geology in engineering. In order to ensure that geological aspects of engineering works are taken into consideration.
Topics of Engineering Geology
Let's understand the topics of Engineering Geology:
- Petrology: Rocks
- Geological structures
- Natural hazards
- Geophysics/Geological masses
- Field tests and measurements, Field techniques: mapping, sampling
- Hydrogeology, Ground improvement: water reservoirs and dams
- Remote Sensing and Geographical Information Systems
- Environmental Geology and Contamination
Petrology: Study of rocks and rock types
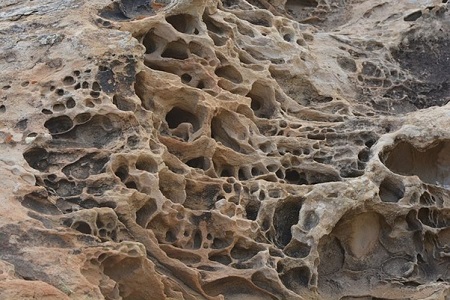
Petrology is the study of rocks, and everything related to the rock's conditions including their formation. Establishing the origins of rocks including their chemical characteristics. Petrology also involves the major branches depending on the main rock types:
- Sedimentary
- Igneous
- Metamorphic.
- Sedimentary:
Sedimentation is the process of settling deposits as sediment. The sedimentary rocks originate with the particles' settlement due to weathering processes like water or air and then other rocks are bound together. Examples of sedimentary rocks are shale, limestone, and sandstone.
- Igneous:
Formation of Igneous rocks is formed when magma cools down and solidifies. In igneous petrology, the scientific study of igneous rocks and its chemical composition and texture is studied.
The crystallisation and different processes of cooling/solidifying are involved. There are two types of Igneous rock that are Extrusive rocks and Intrusive rocks. Rocks that are found on the earth's surface are extrusive rocks and rocks formed beneath the earth's surface are intrusive rocks. Intrusive rocks are also known as plutonic rocks. Examples of Igneous rocks are granite or basalt, and about 95 percent of the earth's crust is covered or made with igneous rocks.
- Metamorphic:
Metamorphic rocks are the formation of existing rocks that are altered by heat, pressure, or reactive fluids. Examples of metamorphic rocks are marble, gneiss, slate, and schist. At first, sedimentary or igneous rocks experience various changes including mineralogical, textural, and chemical changes due to extreme pressure or temperature. These igneous or sedimentary rocks are transformed into metamorphic rocks.
Application of Petrology in Engineering
It is important to understand what are the real-life applications of petrology in Engineering.
- The study of the earth's rocks is a great contribution to developing technological advancement.
- Rocks' study gives a brief about the composition of the earth's crust. Involving understanding of various minerals and chemical properties of rock. Engineering especially in civil engineering depends on the study of rocks.
- Rock study helps to understand the historical formation of the earth's surface. The period of rock formations assists in developing a series of geological events.
- In engineering the use of construction material, minerals are done widely and rock study with understanding important minerals and ores to be used in raw materials by industries.
- Petrology helps the discovery of new minerals and of course increases their supply.
Rock structures
As there are different types of rocks, no rock is in uniform. Rocks are made up of individual minerals made in differ in size, shape, and composition. Rocks are in different sizes from small to big, differentiate on larger scales, and are mostly measured in centimetres to metres to kilometres. Rock structure helps to identify is the rock is igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic. Rock structure is divided into two categories that are "primary" and "secondary" structures.
- Primary also known as elementary structures is formed before or at the same time during the process of transforming to rocks. It helps in determining face, it means which side of the rock represents the upward direction in case of deposition.
- Secondary Structures formed after certain stress, pressure on rocks after they have already formed.
Potential construction material sources
In geology, construction materials are naturally occurring materials like rock and sediment deposits. The common material used in construction is: sand, gravel, crushed stone/aggregates.
Advertisement
Advertisement