Home »
Management Information System
MIS Executive Interview Questions and Answers
Are you looking for the most frequently asked MIS Executive interview questions? This page contains a detailed list of the most popular MIS interview questions and answers asked in any top company's MIS executive interview round.

List of MIS Executive Interview Questions and Answers
The list of some of the common questions asked in an MIS Executive position interview, commonly known as Management Information System Executives.
1) MIS stands for?
MIS stands for "Management Information System".
2) What is MIS?
MIS is a specialized information system that designs as per the needs of an organization. MIS organizes the records, transactions, information, and its transformation within the organization and outside the boundaries of an organization. MIS is a successful system to keep the communication within and outside of the company.
3) What is the purpose of MIS?
The purpose of MIS is to help business executives in decision-making. In the current scenario, MIS is used to make good strategies in the companies, it is not only used in decision making but also helps to find out the key insights from available historical data.
4) What are the major functional areas of MIS?
The major functional areas of MIS are business information system, Manufacturing, Marketing, Quality Assurance, Financial and Accounting, Research and Development, and Human Resource Information Systems.
5) Why companies are using MIS?
MIS is a combination of principles, theories, and practices of management, which play an important role in business organization in the planning and decision-making process.
For more details, read: Overview of MIS
6) What is the role of MIS professionals?
Companies employ information systems at various levels of business to gather, process, and store data. MIS professionals accumulate and disseminate this data in the form of information needed to carry out the daily operations of the business.
7) What are the skills required to be a good MIS professional?
Followings are some of the skills required to be a good MIS professional –
- Good problem-solving abilities,
- Ability to manage time and resources effectively,
- A clear vision of the "big picture" as well as a clear vision of the "small details" a desire to collaborate with others,
- Excellent communication skills,
- The ability to think strategically about technology,
- A desire to take ownership of the development and implementation of their ideas.
8) What are the key significances of MIS?
The significance of a planned, analyzed, designed, and maintained MIS is as follows:
- Helps in progress and growth of the business
- Good management to solve business complexities by providing timely, useful, and reliable information.
- Provides information to the management for taking quick, rational, and speedy decisions.
- Helps in globalization and liberalization of the organizations.
9) What are the career opportunities for MIS professionals?
The career opportunities for MIS professionals are as follows -
- Business Analyst
- Systems Developer
- Technical Support Specialist
- Business Analyst
- Systems Developer
- Network Administrator
- Technical Support Executives
10) What is the nature of MIS?
MIS uses management concepts from various disciplines such as accounting, computing, organizations, management, and operations, because of this interdisciplinary nature of MIS; it is considered both as an art and a science.
11) What are the key characteristics of Management Information System (MIS)?
The characteristics of a Management Information System (MIS) are as follows –
- System approach
- Management-oriented
- As per requirements
- Future-oriented
- Integrated
- Common data flows
- Long-term planning
- Relevant connection of sub-system planning
- Central database
For more details, read: Characteristics of MIS
12) What are the components of Management Information System (MIS)?
The components of a Management Information System are as follows –
- Hardware
- Software
- Organizational Procedures
- Executives
13) What are the major functions of MIS?
The major functions of MIS are as follows –
- To collect useful data
- Data Processing
- Information storage and retrieval
- Disseminating management information
14) What is information storage and retrieval?
MIS stores data as an organizational record and is processed for future use. The data organizes as a field, records, files, and databases for future use. Information retrieval comprises accessing the stored data as per the requirements of the management users. Information retrieval is defined as the process of searching for, retrieving, and serving information to those who have requested it.
Information storage and retrieval system (IS&RS) is a network that includes a built-in user interface that makes it easier to create, search for, and modify data stored on the network. A peer-to-peer network for information storage and retrieval is often administered and maintained by private individuals or independent groups, although it is accessible to the general public.
15) What is disseminating management information?
Information of finished products is categorized and dispersed to the users in an organization as per the needs. This information could be periodic, through reports, or online through computer terminals
For more details, read: Components of MIS
16) What are the key objectives of objectives of a management information system?
The key objectives of a management information system are as follows –
- Data Storage
- Data Retrieval
- Data Propagation
- A system of efficient and effective planning
- Graphical reports
- Controlling the organization
- Standard and budgeted performance
For more details, read: Objectives of MIS
17) How information system is helpful in decision making?
The manager's decision-making plays the main role. It lets management people make decisions based on the information that is being processed. Only input data change, it is an acceptable repeat to support various forms of decision-making by managers. The automation capabilities of MIS can improve your company's performance. MIS is used by managers as a tool to identify the issues facing them. MIS helps managers understand the issues and find solutions.
18) What are the capabilities of MIS?
Management information systems, or MIS, are capable of gathering and storing data from different departments, making valuable reports and presentations that can be used by you and your staff. Besides collecting and processing information, MIS's goals include improving the performance of the company and helping with decision-making.
Following points are shows the capabilities of MIS –
- Enables effective operations of a small business or a large organization
- Decision-making
- Makes possible effective management
- Use of computer
- Supports the hunt for competitive advantage in the marketplace
- Continuous flow
- Complex process
- Enables economic growth by transitioning to newer and more advanced technology
- Future-oriented
- Enables the internationalization of enterprises and enables global competitiveness
- Economical activities
- Perform your work as a management or a professional
- Variety of information
- Flexible approach
- Conduct a firm's activities
- Seek chances in the marketplace for the products of a corporation or of a nation.
19) What is Operational Control?
MIS provides highly reliable and detailed information on a daily or weekly basis to ensure organizational control. For instance, a manufacturing supervisor needs to know if material waste is unnecessary, if expensive overruns are planned, or if the time for a job has expired.
A high volume of timely and accurate information extracted from daily operations is given by MIS.
20) What do you understand by the term middle management?
Middle-level managers need information on issues that impact their divisions, such as rapid drops in revenue, increased demand for a specific product line, large-scale supplier issues, etc. MIS contains summarized information from within the organization as well as from sources outside the organization on these matters. It is not beneficial to have large data in itself; it can even confuse the decision-maker in most instances. In MIS, the basic merit is that if the information is given in a thorough way such that timely, knowledgeable, and rational decisions can be made.
21) What is the role of MIS in top management?
For top executives, MIS offers information for strategic planning and supervision of management. External sources (economic climate, technological developments, competitive changes, etc.) are closely studied and comprehensively evaluated for strategic planning.
22) What is the MIS classification?
MIS classification is a broad concept; this article facilitates you to have a crystal clear understanding of the MIS classification. Here, we categories MIS into three main categories, these are -
- Classification as per Information Characteristics
- Classification as per Application
- Classification as per Business Function
23) Describe MIS classification as per information characteristics.
Based on Anthony's brand of Management, information that is used in commerce trade for decision-making is generally categorized into three types:
- Strategic Information: Strategic information deals with an objective of a house with long-term policy decisions as well as checks provided these objectives are met up to their level or not. For example, acquiring a new plant, a new product, diversification of chain, etc, comes under strategic information.
- Tactical Information: Tactical information deals with the information needed to rule over business resources, like budgeting, bracket control, improvement level, stock level, productivity level, etc.
- Operational Information: Operational information deals with plant/business level information as well as is used to handle proper conduction of specific operational tasks as planned/intended. Various operators specific, machine-specific as well as shift particular jobs for quality authority checks come under this category.
For more details, read: Classification of MIS
24) Describe MIS classification as per as per applications.
MIS classification as per different applications is as follows -
- Planned Information: planned information used in business organizations to maintain specification norms and building strategies.
- Control Information: It is used for controlling the attainment and utilization of important processes in a system.
- Knowledge Information: Knowledge information is acquired through experience and learning and collected from archival data and research studies.
- Organizational Information: Organizational information deals with an organization's environment, where organizational objectives are met. A company reduces its uncertainty by collecting, managing, and using this information carefully.
- Functional/Operational Information: This is operation-specific information where the organization assists to perform its functions of day-day transactions.
- Database Information: It stores large quantities of information that has multiple ownership and application.
25) Describe MIS Classification as per Business Function.
MIS classification as per different business functions are as follows -
- Transaction Processing System: TPS processes transactions and produces reports.
- Management Information System (MIS): As MIS is a well-known information system to organizes the information, which processes data and converts it into meaningful information.
- Decision Support System (DSS): A Decision Support System (DSS) can be inclined with planning, analyzing alternatives, and trial and error search for the solution.
- Executive Support System (ESS): An ESS is specially tailored for the ownership of the chief executive of an association to support his decision-making. It includes various types of decision-making but it is more specific and adult-oriented.
- Office Automation Systems (OAS): Office automation systems are meant to improvements the productivity of frameworks at various levels of management by providing secretarial assistance and better communication facilities.
26) How many levels of management are defined in MIS?
There are three common levels of management in every organization. This can be divided into three groups:
- Upper-level management
- Middle-level management
- Lower-level management
The three levels of management and their core functionalities are described as follows –
-
Upper-level management
- To develop the organization's policies and goals.
- Organizing the enterprise's strategies and assigning good administrators to departments.
- Ensuring proper communication between the organization and the people.
- Issues guidelines for preparing department budgets, policies, and schedules.
- It creates the company's business goals and policies.
- It supervises and oversees the work of all agencies.
-
Middle-level management
The following are the core functionalities of middle-level management in a company:
- To carry out the organization's strategies
- To plan the operations of the department.
- To make preparations for the organization's sub-units.
- To involve with recruiting and give training to lower-level management.
- To translate and describe strategies from upper management to lower management.
- To send essential reports and data to the top level of management.
- To supervise and encourage lower-level managers to boost up their performance.
-
Lower-Level Management
The following are the core functionalities of lower-level management in a company:
- Assigning roles and duties to operational activities.
- To ensure consistency and accountability to ensure production quantity.
- To convey to the workers the firm's priorities and objectives.
- To provide staff with training and guidance daily.
- To provide higher-level supervisors with periodic worker reports.
- To assign roles and responsibilities to staff members.
- To provide day-to-day guidance and instruction to employees.
- To control the quality and quantity of productive products.
- To are also tasked with establishing positive relationships within the company.
- To convey problems, ideas, workers' opinions, and recommendations from employees to higher-level management.
For more details, read: Levels of Management in MIS
27) What Do Information Systems Do for Organizations?
Information systems in companies include systems that:
- Support business activities of the firm
- Support its management
- Work with abstract information rather than with actual things
- Work with abstract information rather than with tangible materials
28) What is MIS design?
Design is one of the most decisive steps of any proposed system. To do a successful design, we follow some necessary steps of system development. MIS design is a strategic process which includes development phases. The phases which are used in MIS design are as follows –
- Problem identification
- Analysis
- Design
- Implementation
- Maintenance
For more details, read: MIS Design
29) What is MIS development?
MIS development is a strategic process of developing an informative information system for a company. To do this, many experts from different levels of a system sit together and investigates and examine a feasible approach to MIS development.
Followings are the different approaches of MIS development–
- Top-down approach
- Bottom-up approach
- Integrative approach
Top-down Approach: In this method, the entire system is partitioned into a hierarchy of subsystems. The overall system is divided into a number of subsystems, which are then divided into a number of other subsystems in a top-down approach.
Bottom-up Approach: As its name implies, this approach mainly starts with the leaf-level or bottom-most management and proceeds progressively to the upper management levels.
Integrative Approach: In the integrative approach subsystems of a system are integrated with each other in such a way so that the objective of the system can be fulfilled.
For more details, read: Approaches of MIS Development
30) What are the limitations of MIS?
Followings are the limitations of MIS:
- MIS is merely a valuable method for top-level executives in making decisions and solving problems.
- MIS can be considered mainly for quantitative factors.
- This has limitations, like its developing cost, employee training time, lack of versatility, and the storage of incorrect or incomplete data.
- MIS implementation may be prohibitively costly.
- The output quality of MIS is directly proportional to the input and process quality.
- Only literate employees are able to work on MIS.
- Technical skills are required to work on MIS.
- Non-programmed decisions are less useful for MIS.
- Depending on the MIS style and functionality, making improvements quickly to represent changing business operations can be impossible.
- MIS is less effective to those organizations, where information is not important and not sharing with others.
31) What is Transaction Processing System (TPS)?
TPS stands for Transaction Processing System. A transaction process system (TPS) is an information processing system for business transactions that collects, modifies, and retrieves all of the data associated with the transaction. It is software that maintains track of transactions by processing the data in an online recording system and storing the results. TPS stands for Transaction Processing System. The Transaction Processing System (TPS) manages the business transactions of the client and therefore helps a company's operations. The performance, dependability, and consistency of a TPS are all important characteristics. Transaction processing (sometimes known as real-time processing) is another term for TPS.
Types of Transaction Processing Systems
There are two types of Transaction Processing Systems –
- Batch processing
- Real-time Processing
Features of Transaction Processing System
A good transaction processing system must have a number of features in order to be effective. A couple of these key features are discussed in greater detail below -
- Performance
- Continuous availability
- Data integrity
- Ease of use
- Modular growth
- Controlled processing
32) What are the key components of Components of Transaction Processing System?
The following are some of the components that make up a TPS:
- Inputs: these are source documents obtained from transactions and used as inputs into the computer's accounting system. Invoices and client orders are examples of inputs.
- Processing: The processing entails the dissection of information provided by the inputs into smaller pieces.
- Storage: This is information that has been preserved in TPS memory and may take the shape of ledgers.
- Output: it is possible to use any record that was generated.
33) What is Decision Support System (DSS?)
A Decision Support System (DSS) is an application for information systems that helps to make decisions. DSS always support to,
- Various decision-making mechanisms and types.
- Effective design and implementation support.
- Semi-structured and unstructured decision-makers.
- Assist at all-level to management.
- Individual and group assistance.
34) What is Executive Information System (EIS?)
An Executive Information System (EIS) is a kind of decision support system (DSS) used in organizations to help executives in decision making. It does so by providing easy access to important data needed in an organization to achieve strategic goals. An EIS usually has graphical displays on a user-friendly interface.
Executive support systems are intended to be used directly by senior managers to support unscheduled strategic management decisions. Often such information is external, unstructured, and even uncertain. Often, the exact scope and context of such information are not known in advance.
This information is based on data,
- Business intelligence
- Financial intelligence
- Data with technology support to analyze
For more details, read: Executive Information System (EIS)
35) What is Expert System in MIS?
An expert system refers to a computer-based information system where knowledge is represented as data and where the processing of the knowledge is driven mostly by computer programs. Expert systems are one of the most modern developments in the field of information technology.
Expert System Components -
The key components of the Expert System are as follows,
- User Interface
- Interference Engine
- Knowledge Base
- Data Acquisition Subsystem
36) What is Office Automation System in MIS?
An office automation system is a mechanism that allows data transformation from one system to another on its own without human interference and inaccuracies. These tools may be used to capture, organize, and process the data to achieve day-to-day activities. It is an automated process, explicitly supporting business activities and processes. Office automation is intended to provide elements that make it possible to simplify, develop, and automate the organization of the activities of a company or a group of people.
An office automation system can be considered as a tool that majorly includes a word processing application, a spreadsheet application, a presentation application, and a database management system.
Features of Office Automation System -
Office automation functionality could include -.
- It eliminates the manual effort to complete basic chores.
- Avoiding mistakes by computers or devices.
- Decreasing the time taken to process an object.
- Provides key insights into the process efficiency metrics.
- Gaining greater access to the method and finding possible bottlenecks.
- Controlling the company by making sound decisions based on results.
- Enhancement in business activities with sound improvement.
- Data organization, storage, and its management.
For more details, read: Office Automation Systems
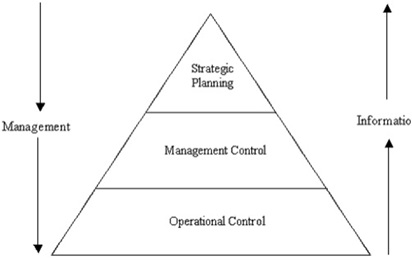
37) What is the Hierarchy of Management Activity in MIS?
Hierarchy is a process of ensuring that specific tasks are carried out effectively and efficiently. Management control is the process by which managers ensure that the resources are obtained and used effectively and efficiently to achieve organizational goals.
The following diagram represents the Hierarchy of Management Activity in MIS,
38) What is a concept of Systems Analysis and Design (SAD) in Management Information System (MIS)?
Systems Analysis and Design is a combination of three individual terms that have their meaning. The meaning of these terms is as follows,
System- A system is an organized group of components linked together to accomplish a specific objective according to a predefined plan.
Analysis- An analysis is a detailed inquiry about a particular problem. It enquires about the answers to all possible questions like what, why, when, how?
Design- It is a blueprint that describes the components and their relationship with a system. There are two types of design - Logical design and Physical design.
39) Why Strategic Management Information System is important?
Strategic management is a detailed set of ongoing activities and procedures that organizations use within an organization boundary to systematically organize and align resources and actions with mission, vision, and strategy.
The Strategic management Information System offers business intelligence and organization as well. If an information system is used in innovative ways to accomplish the objectives and fulfill the organization's mission, TPS, MIS, or any other type of system can be viewed as SMIS activities.
Strategic management activities turn the static plan into a framework that provides decision-making with strategic performance input and allows the plan to adapt and develop as requirements and other factors change. Strategy execution is generally synonymous with the structured execution of a strategy with strategy management practices.
40) What are the key Characteristics of Strategic Management Information System?
The Key Characteristics of a Strategic Management Information System are as follows –
- It helps to prepare a product or service with distinctive characteristics that are competitively appealing in the industry.
- The information system strategy takes into account what knowledge is required to achieve its goals at the strategic and organizational levels of an organization.
- It must be in a position to provide operating productivity, improved benefit, etc.
- It includes interconnecting the activities of an agency that acquires, collects information and eventually provides information.
- This style of approach emphasizes what knowledge is required to achieve business goals.
- It can be used to create new market opportunities by using knowledge tools.
- An IS plan must be capable of fulfilling an organization's (market-oriented) demand.
- It must be functionally oriented (how will the roles, divisions and strategic business units of the company work well?)
- Assists in the study, discovery and creation of consumer niches that have not been adequately filled.
- Information technology is also able to provide a specific niche or segment with the capabilities to identify, extend, and fill. It will be very unique to the industry for the application.
For more details, read: Strategic Management Information System
41) Why do management information systems (MIS) fail?
MIS is a very crucial resource for an organization. MIS failures can create a big negative impact on the company that has designed it. MIS failure is very expensive for the company in terms of money wastage, time wastage, resource wastage, etc. So, the organization needs to identify the root causes of MIS failure and be alert to these concerns during the development of MIS.
Followings are the main root causes of MIS failure may arise due to followings -
- Incomplete analysis – incomplete analysis is the biggest cause of system failure. An incomplete analysis is due to some common reasons like problem identification is not properly defined, key requirements and constraints are not properly understood and identify at the early stages of the MIS design and development process.
- Lack of management involvement –Lack of management involvement have long-lasting consequences and can impact an entire system. Many executives who are not personally involved in MIS system design would most likely is a cause of system failure.
- The accent of the computerized system – if someone doesn't understand the procedures and its need for handling input and output system, hardware and its usage, and application and its impacts; makes the biggest cause of MIS failure.
- Concentration on low-level data processing – Information must be easily accessible and understood.
- Lack of management knowledge of ICT systems and capabilities –the implementation and use of ICT to enhance and encourage knowledge management. Managers know what they want from the system but don't understand the technology
- Lack of teamwork –During MIS design, An ICT director must organize the divisions of accounts, marketing, distribution, etc. to help everybody understand the benefits of the system.
- Lack of professional standards –All systems require simple documentation that can be understood by all users.
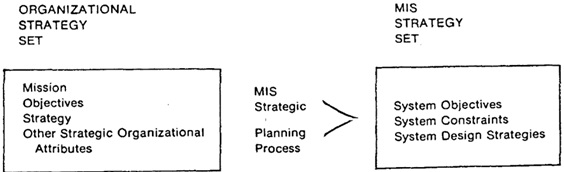
42) What is the Strategic Planning for MIS?
Strategic planning for MIS is a managerial activity that enhances the working process and prospects of an organization. For strategic planning and management, there are many structures and methodologies to choose from. Although there are no hard and fast rules when it comes to choosing the right system, the majorities of them follow a similar trend and share similar characteristics.
Advertisement
Advertisement