Home »
Python
Scalar Multiplication Property 1 | Linear Algebra using Python
Linear Algebra using Python: In this article, we will learn more about scalar multiplication in Vectors and how to code?
Submitted by Anuj Singh, on May 10, 2020
Prerequisite: Linear Algebra | Defining a Vector
Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning linear equations by using vector spaces and through matrices. In other words, a vector is a matrix in n-dimensional space with only one column. In a scalar product, each component of the vector is multiplied by the same scalar value. As a result, the vector's length is increased by a scalar value.
For example: Let a vector a = [4, 9, 7], this is a 3-dimensional vector (x, y, and z)
So, a scalar product will be given as b = c*a
Where c is a constant scalar value (from the set of all real numbers R). The length vector b is c times the length of vector a. This scalar, multiplication follows a property shown below:
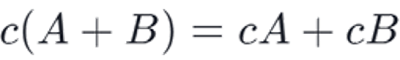
Where A and B are two vectors. The python code aims to evaluate the right-hand side and left-hand side for proving the scalar property.
Python code for Scalar Multiplication Property
# Vectors in Linear Algebra Sequnce
A = [3, 5, -5, 8]
B = [7 , 7 , 7 , 7]
print("Vector A = ", A)
print("Vector B = ", B)
C = int(input("Enter the value of scalar multiplier: "))
# defining a function for scalar multiplication
def scalar(C, a):
b = []
for i in range(len(a)):
b.append(C*a[i])
return b
# defining a function for addition
def add(a,b):
c = []
for i in range(len(a)):
c.append(a[i]+b[i])
return c
# RHS
ss = add(A,B)
print("Vector C(A + B) = ", scalar(C,ss))
# LHS
An = scalar(C, A)
Bn = scalar(C, B)
print("Vector (CA + CB) = ", add(An,Bn))
print('---Both are same and therefore,')
print('the scalar property in vectors satisfies')
print('this property---')
Output
Vector A = [3, 5, -5, 8]
Vector B = [7, 7, 7, 7]
Enter the value of scalar multiplier: 3
Vector C(A + B) = [30, 36, 6, 45]
Vector (CA + CB) = [30, 36, 6, 45]
---Both are same and therefore,
the scalar property in vectors satisfies
this property---
Advertisement
Advertisement