Home »
C/C++ Data Structure Programs
Clone a linked list with next and random pointer using C++ program
In this tutorial, we will learn how to clone a linked list with the next random pointer? This tutorial contains a problem statement, explanation, algorithm, C++ implementation, and output.
By Souvik Saha Last updated : August 02, 2023
Problem statement
Given a linked list, there are two node pointers one point to the next node of the linked list and another is the random pointer which points to any random node of that linked list. Your task is to make a clone a linked list of that linked list.
Example
Input:
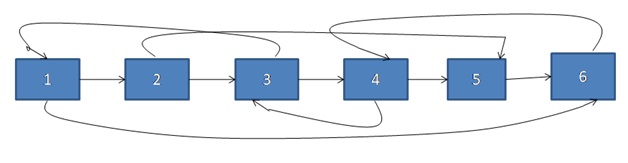
Output
Make a same copy of that linked list.
Algorithm
Node structure for random pointer:
Node temp
{
Int data;
Node* next;
Node* random=NULL;
}
To solve that problem we follow this algorithm:
- First, we copy the next pointers and make a linked list.
- In the second iteration, we copy the random pointers of that linked list.
Using this algorithm the time complexity is O(n).
C++ program to clone a linked list with next and random pointer
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
node* next;
node* random;
};
//Create a new node
struct node* create_node(int x)
{
struct node* temp = new node;
temp->data = x;
temp->next = NULL;
temp->random = NULL;
return temp;
}
void push_random(node* head, int x, int y)
{
struct node* temp1 = head;
while (temp1) {
if (temp1->data == x) {
break;
}
temp1 = temp1->next;
}
struct node* temp2 = head;
while (temp2) {
if (temp2->data == y) {
break;
}
temp2 = temp2->next;
}
temp1->random = temp2;
}
//Enter the node into the linked list
void push(node** head, int x)
{
struct node* store = create_node(x);
if (*head == NULL) {
*head = store;
return;
}
struct node* temp = *head;
while (temp->next) {
temp = temp->next;
}
temp->next = store;
}
//Reverse the linked list
struct node* copy(node* head)
{
struct node* temp = head;
struct node* store = create_node(0);
struct node* curr = store;
while (temp) {
curr->next = create_node(temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
curr = curr->next;
}
temp = head;
curr = store;
while (temp) {
curr->random = temp->random;
curr = curr->next;
temp = temp->next;
}
store = store->next;
return store;
}
//Print the list
void print(node* head)
{
struct node* temp = head;
while (temp) {
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
}
int main()
{
struct node* l = NULL;
push(&l, 1);
push(&l, 2);
push(&l, 3);
push(&l, 4);
push(&l, 5);
push(&l, 6);
srand(time(0));
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) {
int r = (rand() % 6) + 1;
push_random(l, i, r);
}
cout << "Original list" << endl;
print(l);
struct node* c = copy(l);
cout << "\nCopy list" << endl;
print(c);
return 0;
}
Output
Original list
1 2 3 4 5 6
Copy list
1 2 3 4 5 6
Advertisement
Advertisement