Home »
Full Forms »
IT Full Forms
What is the full form of HTTP?
Full form of HTTP: Here, we are going to learn about the HTTP, its full form, what is HTTP, how HTTP works, its advantages and disadvantages.
By Anushree Goswami Last updated : March 26, 2024
HTTP: Hypertext Transfer Protocol
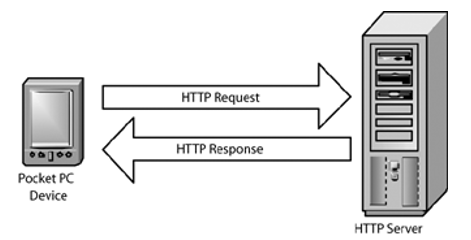
HTTP is an abbreviation of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol. Hypertext Transfer Protocol is an application layer protocol that contains a set of instructions used for transferring distributed information system files, multimedia data communication on the World Wide Web. It is the fundamental substructure of data communication for the World Wide Web. It makes available to use a level of quality for web browsers that enables users, over the internet to exchange information. HTTP is utilized by the majority of the websites to ingress any file or page. In the client-server computing model, HTTP is a request-response protocol. It is developed within the foundation of Internet Protocol Suite as an application layer protocol.
What is Hypertext?
A hypertext is a text which contains a connection link inside it. On a webpage, if a user clicks on a word and if it redirects a user on a new web page, then it shows that a user has clicked on a hypertext link.
How HTTP works?
When a user wants to access any specific file or page and enters a URL in his web browser, then the browser constructs an HTTP request and sends it to the Internet Protocol address (IP address) specified by the URL, and then the protocol extract information from the server and responses back that requested web page to the client. A user requires to put HTTP before the address of the page.
Advantages
- Without having to inquire the sender what application must be used to read or view the contents of the file, this allows the application which is at receiving end to rapidly access the incoming file.
- HTTP allows more than one connection links to download different contents or material simultaneously, therefore it speeds up the transmission of data on a browser server.
- Mapping IP addresses to simply in an easier manner identify names, made the World Wide Web economically feasible.
- The user has the choice of rapidly downloading extensions or plug-ins if further abilities are required to expose to view the data. These add-ons comprise Flash players and PDF documents, readers.
Disadvantages
- A user can get a threat to his privacy because the Information sent through HTTP by the user is not encrypted.
- Packet headers are greater in size than other protocols as they are required for the purposes of security and quality assurance of the information being transferred.
- HTTP is slower than other native protocols.
- Information sent by a user through a browser can leave unprotected his system of the computer to virtual threats.
Advertisement
Advertisement