Home »
MySQL
MySQL FOREIGN Key
MySQL | FOREIGN Key: Learn about the MySQL FOREIGN Key, with its explanation, syntax, and query examples.
Submitted by Apurva Mathur, on September 15, 2022
FOREIGN Key
FOREIGN Key is a key that is used to establish the relationship between two tables.
Suppose we have two tables named "Country" and "States". These tables have the following attributes:
- Country: Country_ID, Country_name.
- State: State_ID, Country_ID, State_name
Where "Country_ID" in the "Country" table is the primary key and "State_ID", in the "State" table is the primary key.
From these attributes, you'll observe that the "State" table is related to the "Country" table through the attribute "Country_ID". This is the main concept of the foreign key, the foreign key creates a relationship between two tables. Now, in this case, "Country_ID" act as a foreign key in the "State" table,
Let us see this in detail,
Table: Country
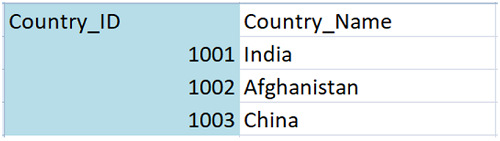
Here in this table, we have country id and country name.
Table: State
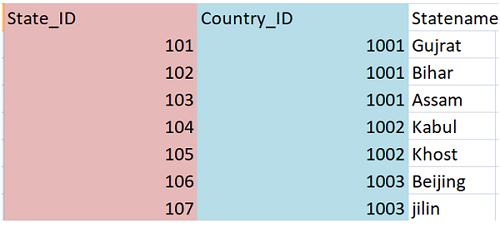
This is "State" table, as we can see in this table; all the countries are linked with country_ID.
So for example if I want to know the country name of state_ID 107 then I can just simply see the country_ID it is associated with. Here country_ID would be 1003 and we’ll see country_name in country table where country _ID is 1003 we’ll get our country, i.e. China.
With the help of a foreign key we can get the information from another table.
FOREIGN Key Syntax
CREATE TABLE table_name(
FOREIGN KEY (Column_name) data type references table_name(column_name)
);
FOREIGN Key Examples
CASE 1: Creating foreign key
Now, let us just take the above example, here I am making two tables, "Country" and "State", and as stated above "Country" table will be having Country_ID (primary key) and Country_Name as its two columns of this table, whereas the "State" table will be having three columns named as state_ID (primary key), Country_ID (foreign key) and Statename.
CREATE TABLE country (
`country_id` INT NOT NUL PRIMARY KEY,
`country_name` VARCHAR (45) NULL
);
CREATE TABLE state (
`state_id` INT NOT NUL,
`country_id` INT,
`state_name` VARCHAR (45) NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (state_id),
FOREIGN KEY (country_id) REFERENCES country (country_id)
);
And this is how we create foreign key while creating a table.
CASE 2: Making a foreign key after table creation using alter statement
In this case, we will use the following syntax,
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD FOREIGN KEY (column_name) REFRENCES table_name (column_name);
CASE 3: Deleting an existing foreign key
In this case, we will use the following syntax,
ALTER TABLE table_name
DROP FOREIGN KEY FK_(column_name);
Advertisement
Advertisement