Home »
C programs »
C stdio.h library functions programs
fopen() function in C language with Example
Here, we are going to learn about the fopen() function of library header stdio.h in C language with its syntax, example.
Submitted by Souvik Saha, on January 09, 2019
fopen() function in C
Prototype:
FILE *fopen(const char* filename, const char* mode);
Parameters:
const char* filename, const char* mode
Return type: FILE*
Use of function:
The fopen() function opens a stream which links with a file. The prototype of this function is: FILE *fopen(const char* filename, const char* mode);
Where,
- filename: Name of the file which you want to work.
- mode: The operation modes like read, write etc.
fopen() example in C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
//create two files pointer
FILE *f1, *f2;
char s[20];
//open file for reading
f1 = fopen("includehelp.txt", "w");
printf("File is created for write operation\n");
printf("Enter any string\n");
scanf("%s", &s);
//enter the string into the file
fputs(s, f1);
fclose(f1);
//append file for further operation
f2 = fopen("includehelp.txt", "a");
printf("File is appended\n\n");
fprintf(f2, "%s", "_tutorial");
fclose(f2);
//check the file's existence
if ((f2 = fopen("includehelp.txt", "r")) == NULL) {
printf("file cannot open\n");
exit(1);
}
//read the content from the file
fscanf(f2, "%s", s);
printf("%s", s);
fclose(f2);
return 0;
}
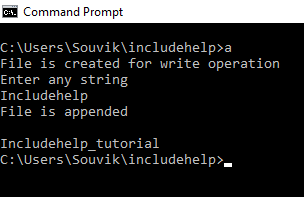
Output
C stdio.h Library Functions Programs »
Advertisement
Advertisement