Home »
Python »
Python Programs
Boolean Indexing in Pandas
Let's understand Boolean Indexing in Pandas with examples.
By Pranit Sharma Last updated : September 21, 2023
Indexing in Pandas
Index in pandas is just the number of rows defined in a Series or DataFrame. The index always starts from 0 to n-1 where n is the number of rows. The index is used in indexing which is a method of traversing or selecting particular rows and columns or selecting all the rows and columns.
Boolean Indexing
In programming, we sometimes use some specific values that only have two values, either True or False. These values are known as Boolean values. Boolean Indexing in Pandas is nothing but indexing the rows of the pandas DataFrame with their actual values (True or False) rather than naming them with a string or an integer value.
Performing Boolean Indexing in Pandas
To achieve Boolean indexing, we simply assign a list of Boolean values to the index values while defining a DataFrame.
Note
To work with pandas, we need to import pandas package first, below is the syntax:
import pandas as pd
Let us understand with the help of an example.
Create and print the dataframe
# Importing pandas package
import pandas as pd
# Creating a dictionary
d = {
'Name':["Ayushi", "Parth", "Sudhir", "Ganesh"],
'Post': ["HR", "SDE", "Data-Analyst", "SDE"],
'Salary':[40000, 50000, 80000, 52000]
}
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(d, index = [True, False, True, False])
# Display original DataFrame
print("Original DataFrame:\n",df,"\n")
The output of the above program is:
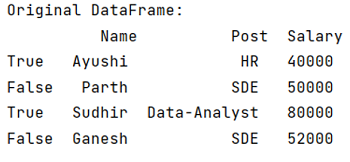
Performing Boolean indexing in Pandas
We can also access any of the subsets of this DataFrame with the condition of True or False, if the True value is passed, the subset having values True will be resulted otherwise subset having the value False will have resulted.
# Accessing a subset having value True
print(df.loc[True])
The output of the above program is:

Python Pandas Programs »
Advertisement
Advertisement