Home »
C programming language
Precedence and associativity of Arithmetic Operators in C language
Last Updated : December 17, 2025
While, writing programs in C, we mostly perform calculations and arithmetic operations using the C arithmetic operators. Even the basic addition program in C involves the use of arithmetic addition operator + to perform addition of two integers or float value.
Precedence and associativity of Arithmetic Operators in C
The asterisk * indicates multiplication and the forward slash (/) denotes the division operator. Unlike algebra, in C, to multiply a times b, the multiplication must be explicitly denoted by using the * operator, as in a * b. The arithmetic operators are all binary operators. For example, the expression 3 + 7 contains the binary operator + and the operands 3 and 7, or - operator subtracts the second operand from the first.
C also has special % modulus operator, which returns the remainder of two numbers. It can be used cleverly in programs such as finding a number whether it is even or odd.
But, when operators are used in a composite expression, then the values might not be what you expect.
Example
Consider this example,
a = 10 + 2 * 5 - 6 / 2
If you think its 27, then you are tricked by C. All mathematical operations form a hierarchy based on priority which is shown below. In the above calculation the multiplication and division parts will be evaluated first and then the addition and subtraction parts. This gives an answer of 17.
Table of Precedence and associativity of Arithmetic Operators
The image below illustrates the precedence and associativity of arithmetic operators:
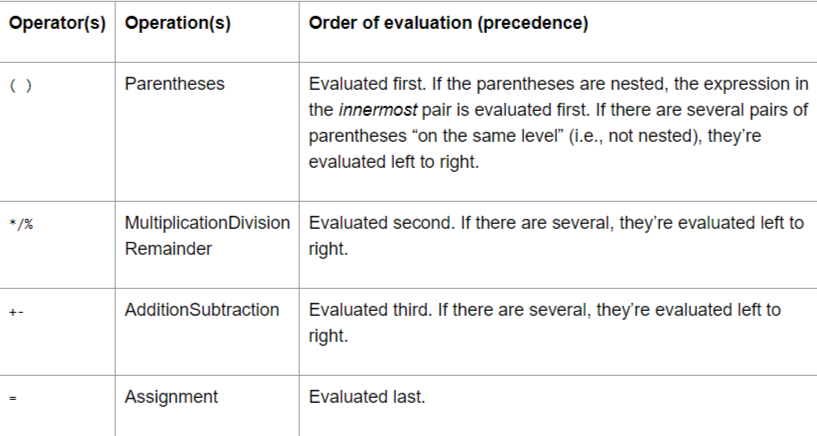
According to this table, from the left to right, the operator with higher precedence will get evaluated first. If two operators have same precedence, then the one which occurs first from left to right will get evaluated first. The parentheses have highest priority, which means expressions inside them are evaluated first. Parentheses can contain sub parentheses and the rule follows same for every operator.
Here are a few examples to help you better,
a = 16 + (2 * 5) - (6 / 2) // Answer: 23
a = (10 + 2) * (8 - 6) / 2 // Answer: 12
a = 15 + (4 * 12 / 6) - 3 // Answer: 20
Associativity clarification
Operator associativity determines the direction (left to right or right to left) in which operators of the same precedence are evaluated. Most arithmetic operators in C follow left-to-right associativity, meaning the expression is evaluated from left to right when precedence is equal.
a = 20 / 5 * 2 // Evaluated as (20 / 5) * 2 = 8
Unary Operators and Their Precedence
Unary operators such as unary minus (-a) have higher precedence than binary arithmetic operators. This means they are evaluated before multiplication, division, addition, or subtraction.
a = -10 * 2 // Result: -20
Common Mistakes Due to Operator Precedence
A common mistake made by beginners is assuming that expressions are evaluated strictly from left to right without considering operator precedence. This often leads to incorrect results in complex arithmetic expressions.
Using parentheses can help avoid such logical errors and make expressions easier to understand.
Best Practices While Using Arithmetic Operators
To write clean, readable, and error-free code, it is always recommended to use parentheses even when you are confident about operator precedence rules. Parentheses clearly define the intended order of evaluation and improve code maintainability.
Why Understanding Operator Precedence Is Important
Understanding the precedence and associativity of arithmetic operators in C is essential while writing mathematical formulas, conditional expressions, and performance-critical programs. A small mistake in evaluation order can lead to incorrect program logic.
C Arithmetic Operator Precedence Exercise
Select the correct option to complete each statement about precedence and associativity of arithmetic operators in C.
- In C, which arithmetic operator has the highest precedence?
- If two arithmetic operators have the same precedence, C evaluates them based on:
- What will be the result of the expression
20 / 5 * 2 in C?
- Which operator is used to find the remainder of a division in C?
- To avoid ambiguity in complex arithmetic expressions, programmers should use:
Advertisement
Advertisement