Home »
Computer Graphics
Color Cathode Ray Tube in Computer Graphics
Computer Graphics | Color Cathode Ray Tube: In this tutorial, we are going to learn about the Color Cathode Ray Tubes and how Color Cathode Ray Tube is different from normal CRTs?
By Monika Sharma Last updated : April 05, 2024
Color Cathode Ray Tube
CRT i.e. Cathode Ray Tubes are used to produce Color displays. The basic methodology or principle of producing Colored displays is by combining the three basic colors which are: red, blue and green. By choosing different combinations of these three basic Colors we can produce many colors in fact, all the colors to be displayed. The basic methodology or idea behind this must be the technique and knowledge to combine these colors in perfect ratio to produce the colors required.
This could be done through techniques such as:
- Beam penetration method: This CRT is similar to the basic CRT, the only difference is that it makes use of multi Colored phosphorus consisting of the number of layers. Each phosphorus layer is responsible for only one Color. All other arrangements are similar to the basic or simple CRT. But the thing is that it can produce only a maximum of 4 to 5 colors.
- Shadow mask method: The shadow mask CRT, as in basic CRT instead of using one electron gun, uses 3 different guns placed one to the side of the other forming a triangle or a Delta. Each particular pixel point displayed on the screen is also made of 3 different types of phosphors to produce the basic red, blue and green Colors. Just before the phosphor screen is a metal screen, it is called a shadow mask.
Working of Color Cathode Ray Tube
The working of the cathode ray tube depends upon the movement of the beam of electrons. The electron guns which are present at the rear end of the cathode ray tube produce a high sharp beam of electrons which is highly accelerated by making them pass through high voltage. These highly accelerated beams of the electron when hits the fluorescent screen with full velocity produce illuminated spots.
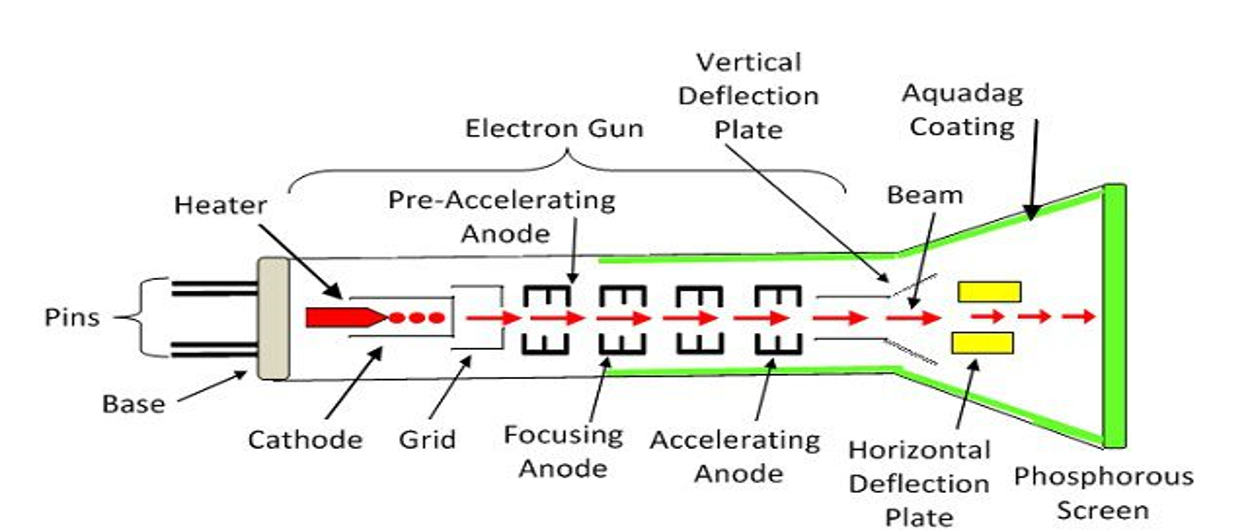
Cathode Ray Tube
Image source: https://circuitglobe.com/cathode-ray-tube-crt.html
As the electrons are made to eject from the electron gun, the beam passes through the deflection plates present in the cathode ray tube. These plates deflect the beams produced as they have voltage applied across the two of them. Due to this voltage difference, the beams are deflected. These plates are placed on top of another thus, deflecting the beam upwards and downwards with the help of respective plates according to the potential difference applied. The horizontal and the vertical deflection of beams are independent of each other thus producing no effect in the positioning of the plates. They can be present anywhere in the cathode ray tube keeping in mind that they fall in the line of the electron beam. All the working parts of a CRT are enclosed in a vacuum glass envelope such that the emitted electron beam can easily move freely from one end of the tube to the other end.
Applications of Color Cathode Ray Tube
- It is used in televisions.
- In various computer monitors to display out the Colors.
- As a display device in the radar.
- It is used in a cathode ray oscilloscope.

An oscilloscope: application of cathode ray tube.
Advantages of using CRT
- It produces high resolution.
- It gives Color and greyscale accuracy.
- It is a cost-efficient device.
- It has a high resolution and aspect ratio giving a tremendous amount of good performance
Disadvantages of using Cathode Ray Tube
- It is relatively bright but not bright as LED.
- They are very large, bulky and heavy. Consumption of electricity is very high which leads to the production of a tremendous amount of heat.
- CRT's give disturbing patterns on the screen.
- Their shape is also a problem. Some are spherical or round in shape while the newer ones are flat which makes them easy to handle and carry.
Advertisement
Advertisement