Home »
Computer Network
What are Synchronous and Asynchronous Transmission?
In this tutorial, we will learn about the synchronous and asynchronous transmission, their characteristics, advantages, and disadvantage.
By Monika Jha Last updated : May 05, 2023
Serial Data transmission can occur in two methods,
- Asynchronous Transmission
- Synchronous Transmission
What is Asynchronous Transmission?
It is named Asynchronous transmission because the timing of a signal is unimportant. In this transmission process transmitted information is encoded with start and stop bits, specifying the beginning and end of each character. As long as some pattern is followed, the receiving device can retrieve the information without regard to which it is sent.
Patterns are based on grouping the bitstreams into a byte usually eight bits is sent along with the link as a unit. The sender sends each group of data independently, relaying it to the link whenever ready, without regard to a timer.
- The receiver cannot use timing to predict the arrival time of the next group so that synchronizing pulse is required. To notify the receiving system to the arrival of a new group, therefore, an extra bit is added to the beginning of each byte.
- This 0s bit is referred to as the start bit. Telling the receiver that the byte is finished, one or more additional bits are appended to the end of the byte. This is bit is called a stop bit.
- By this method, each byte is increased in size to at least 10 bits, of which 8 are information and two or more are signals to the receiver.
- Also, the transmission of each byte may gap of varying duration. This gap between information can be represented either by an idle channel or by a stream of additional stop bits.
- The bits of a byte that is 8 bits are transmitted simultaneously on separate wires. If two devices are close together computer or printer so the communication within the computer.
Examples
Examples of Asynchronous Transmission: emails, forums, letters, radios and televisions.
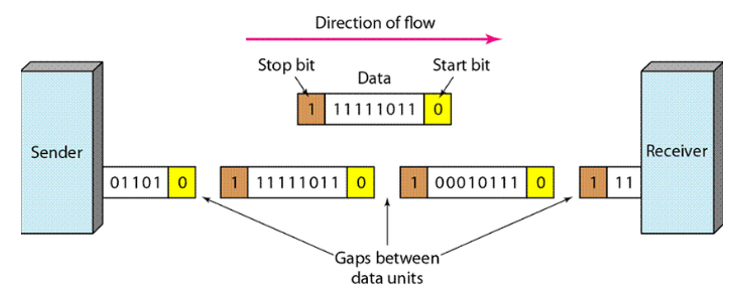
Asynchronous Transmission
This figure shows the schematic illustration of asynchronous transmission. In this example, the start bits are 0s and the stop bits are 1s and the gap is represented by an idle line rather than by additional stop bits.
In this diagram, the ASCII character would be transmitted using 10 bits. In this transmission scheme "0100 0001" changes into "1 0100 0001 0". The extra bits, depending on the parity bit, at the start and end of the data transmission.
This starts and stops bits tells the receiver that character is coming and also the character has ended.
This scheme of transmission is used when data are transmitted irregularly as opposed to in a solid stream.
Characteristics
The following are the characteristics of asynchronous transmission:
- Extra bits are added to the start and end of the character stream.
- Between two characters there may exist gaps or spaces.
- The idle time is not constant between bytes as only one byte is sent at a time.
- The reception of data is done at different clock frequencies.
Advantages
The following are the advantages of asynchronous transmission:
- Synchronization between devices is not necessary.
- It is a low-cost scheme.
Disadvantages
The following are the disadvantages of asynchronous transmission:
- Low transmission due to the use of 'start' and 'stop' bits and gaps between data chunks.
- Timing errors take place.
What is Synchronous Transmission?
The bitstreams are combined into longer "frames" in synchronous transmission, which may contain multiple bytes. Each byte, however, is introduced onto the transmission link without a gap between it and the next one.
It is left to the receiver to separate the bitstreams into bytes for decoding purposes.
- In other words, data or information is transmitted in the form of an unbroken string of 1s and 0s, and the receiver separates that string into the bytes or characters, it needs to reconstruct the information.
- In this transmission, we send bits one after another without start/stop bits or gaps. Grouping of bits is the receiver's responsibility.
Examples
Examples of Synchronous Transmission are chat rooms, video conferencing, telephonic conversations, face-to-face interactions, etc.
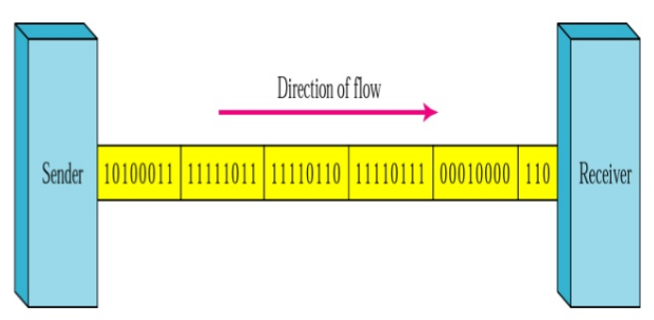
Synchronous Transmission
Characteristics
The following are the characteristics of synchronous transmission:
- Between transmitted characters, there are no spaces.
- Timing is very important as the accuracy of the received information is completely dependent on the ability of the receiving device to keep an accurate count of the bits as they come in.
- Special 'syn' characters are sent before the data being sent.
- These syn characters are placed between chunks of data for timing functions.
Advantages
The following are the advantages of synchronous transmission:
- Data speed is much higher because of no extra bits at the sending end and at the receiving end.
- Timing errors are reduced due to syn.
- More useful for high-speed applications.
Disadvantages
The following are the disadvantages of synchronous transmission:
- Timing is responsible for the accuracy of data
- It is required that transmitter and receiver be properly synchronized