Home »
Golang
Loops in Go Language
Last Updated : April 19, 2025
In programming, loops are special blocks of code that are used to execute the given block of code continually till the given condition becomes true.
Golang supports loops. But Golang has only one type of loop which is the for loop. We can use this for loop in multiple ways and perform all sorts of tasks in Golang using this.
Go for Loop
The for loop is a counter-controlled loop whose number of repetitions is definite. This for loop can be used in different syntaxes to perform tasks similar to other types of loop.
Flow Chart
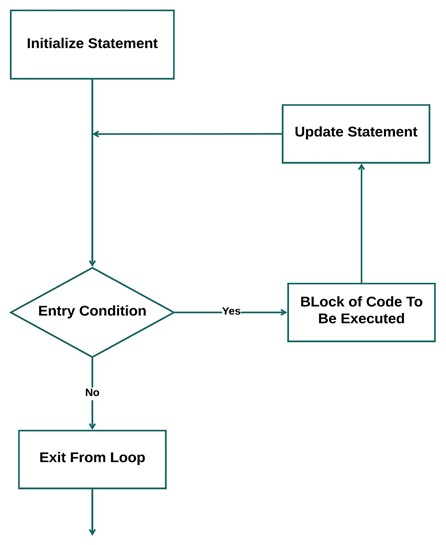
Syntax
for initialization ; condition ; updation {
// block of code to be executed
}
Explanation
The parts of the for loop are,
- Initialization statement: The initialization statement is used to declare the variables that will be used for iteration.
a := 4
- Condition statement: This statement contains the test condition which evaluates to a boolean value using which the entry to the loop.
a > 0
- Updation statement: The update statement is used to update the initialized value to perform the loop operation.
a--
- Code block: The block of code (statement) to be executed multiple times in the for loop.
print(a)
All the parts of the loop are optional, we can update the syntax in order to make the code perform the way we want it to work.
Let's see all of them.
As standard for loop
The general syntax of for loop in Go is similar to what we study in other programming languages like C, C++, etc.
Syntax
for initialization ; condition ; updation {
// block of code to be executed
}
Golang program to use of simple for loop
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Printf("Table of 2 \n")
for a := 1; a <= 10; a++ {
fmt.Printf("2 * %d = %d\n", a, (2 * a))
}
}
Output:
Table of 2
2 * 1 = 2
2 * 2 = 4
2 * 3 = 6
2 * 4 = 8
2 * 5 = 10
2 * 6 = 12
2 * 7 = 14
2 * 8 = 16
2 * 9 = 18
2 * 10 = 20
As while loop
We can use the for loop in Golang to perform a while loop. For this, we will keep only the test condition of the loop which will control the entry to the loop. The initialization, in this case, will be done before the loop starts and the update will be made inside the body of the loop.
Syntax
for condition statement {
// code to be executed
}
Golang program to illustrate the working of for loop as while loop
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Printf("Table of 2 \n")
x := 1
for x <= 10 {
fmt.Printf("2 * %d = %d\n", x, (2 * x))
x++
}
}
Output
Table of 2
2 * 1 = 2
2 * 2 = 4
2 * 3 = 6
2 * 4 = 8
2 * 5 = 10
2 * 6 = 12
2 * 7 = 14
2 * 8 = 16
2 * 9 = 18
2 * 10 = 20
for loop on a range
The for loop can also be used to iterate over a range of numbers. For this, we have a bit different syntax where we have the range as the test and update condition of the for loop.
Syntax
for i, j := range {
// code to be executed
}
Golang program to illustrate the working of for loop as Range
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
intArray := []int{4, 7, 1, 9}
for i, j := range intArray {
fmt.Printf("Element %d = %d\n", (i + 1), j)
}
}
Output:
Element 1 = 4
Element 2 = 7
Element 3 = 1
Element 4 = 9
This type of conversion is used to iterate over collections in Golang. The collections that can be iterated using Array, String, Map, Channel.
Infinite for Loop
The for loop in Golang can also be converted to an infinite loop by omitting all the statements that are passed while calling the loop.
Syntax
for{
// Code to be Executed
}
Golang program to illustrate the working of for loops as infinite loop
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
for {
fmt.Printf("This is an infinite Loop...\n")
}
}
Output:
This is an infinite Loop...
This is an infinite Loop...
This is an infinite Loop...
This is an infinite Loop...
This is an infinite Loop...
This is an infinite Loop...
This is an infinite Loop...
This is an infinite Loop...
This is an infinite Loop...
This is an infinite Loop...
This is an infinite Loop...
.
.
.
Infinite times...
Go Loops Exercise
Select the correct option to complete each statement about loops in Go.
- The ___ loop is the only loop available in Go.
- The ___ statement is used to exit a loop prematurely in Go.
- The ___ statement is used to skip the current iteration of a loop and move to the next iteration in Go.
Advertisement
Advertisement