Home »
Operating System
Booting Process in Operating System
Last Updated : December 30, 2025
What is Booting Process?
When our computer is switched on, It can be started by hardware such as a button press, or by software command, a computer's central processing unit (CPU) has no software in its main memory, there is some process which must load software into main memory before it can be executed.
After the computer is turned on, a specific program needs to load in the computer's main memory which is Operating System.
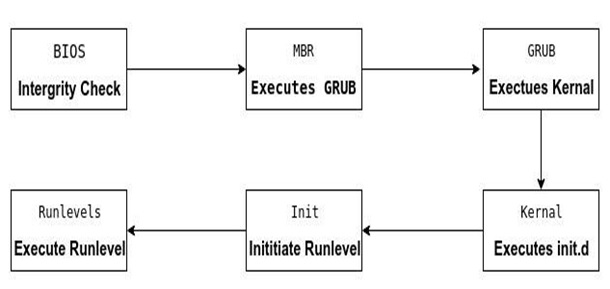
In the Booting process, System will check all the hardware's and Software's those are installed or attached with the system and all the Files those are required for running a system, also loads into memory.
ROM also reads the information stored in these files.
At the Time of Booting all Instructions will be read required to start the system.
OS holds the following processes at the time of booting:
Categories of Booting Process
There are two categories of Booting process,
- Hard (Cold) Booting
- Soft (Warm) Booing
1. Hard (Cold) Booting
Restart a computer is referred to as rebooting, It can be "hard" or "cold", e.g. after power to the CPU is switched from off to on. In this category of booting the computer starts from a completely dead state.
For instance, When we press the Power Button, the system starts with its initial state. It reads all the information that is stored in the Read-Only Memory (ROM) and automatically the Operating System will be loaded into the system's main memory.
2. Soft (Warm) Booing
In "soft" or "warm" booting, the power is not cut. In some systems, a soft boot may optionally clear RAM to zero.
What is POST (Power On Self Test)?
- The Power On Self Test happens each time after turn on your computer.
- It is a diagnostic testing sequence for all the hardware devices. It checks hardware device availability. It sends a signal to all the hardware devices and they send an acknowledgment back to it. If an acknowledgment is sent by that device then that device is working, if not then it will be removed from the system.
- If there is any error then a beep like sound generates or some error messages displays on the monitor. These beeps are referred to as POST beep codes.
What is Master Boot Record?
- The Master Boot Record (MBR) is the information which is in the first sector of any hard disk that indicates how and where an operating system is located so that it can be boot (loaded) into the computer's main memory or random access memory.
- The MBR is also sometimes referred to as the "partition sector" or the "master partition table". It has only four primary partitions. We can create more partitions by setting the fourth partition as the extended partition and also we can create sub-partitions (or logical drives) within it.
- It holds information about GRUB (or LILO in old systems).
-
Its size is less than 512 bytes. It has three components
- primary boot loader information in 1st 446 bytes.
- partition table information in next 64 bytes.
- MBR validation checks in the last 2 bytes.
What is init?
This is the last step of the booting process. It decides the run level by looking at the / etc / inittab file.
- The initial state of the operating system decides by the run level.
- Following are the run levels of Operating System:
Level
0 - System Halt
1 - Single user mode
2 - Multiuser, without NFS
3 - full multiuser mode
4 - unused
5 - Full multiuser mode with network and X display manager(X11)
6 - Reboot
- We would set the default run level to either 3 or 5.
- We can execute 'grep initdefault / etc/ inittab' on your system to identify the default run level.
- Init uses run levels to load all appropriate program.
The step after is to start up various daemons that support networking and other services. X server daemon manages display, keyboard, and mouse. You can see a Graphical Interface and a login screen is displayed during X server daemon is started.
Failure During Boot
If the computer cannot boot, we will get a boot failure error. This error indicates that the computer is not passing POST or a device in the computer, such as the hard drive or memory, has failed.
You may also hear a beep code to identify which hardware is failing during the POST.
An error message or blue screen may show on the screen as operating system files cannot be loaded, due to not being found or being corrupt.
Advertisement
Advertisement