Home »
Operating System
Cache Memory: What It Is, Types, Advantages, and Disadvantages
Last Updated : December 30, 2025
What is Cache Memory?
Some kinds of memory are designed for long-term use to store information. All kinds of memory are important to running our computer smoothly in terms of both software and hardware. Cache Memory is a special very high-speed memory and it is volatile. It is used to speed up and synchronizing with high-speed CPU and Cache memory is costlier as compared to main memory or secondary memory but economical than CPU registers.
- Cache memory is an extremely fast memory type so that it provides high-speed data access to a computer microprocessor.
- Cache splits into L1d (for data) and L1i (for instructions) and almost all current CPUs with caches have a split L1 cache.
- It acts as a high-speed buffer between RAM and the CPU, it is close to the CPU that results in fast data transfer.
- If the capacity of the cache is larger so that can store more data and faster it can operate. Conversely, chips with much lower capacity perform slower given they don't store as much data.
- Cache memory is used for storing the data which is given by the user as input and is necessary for the computer microprocessor to perform a task that is it keeps frequently requested data and instructions so that they are immediately available to the CPU when needed.
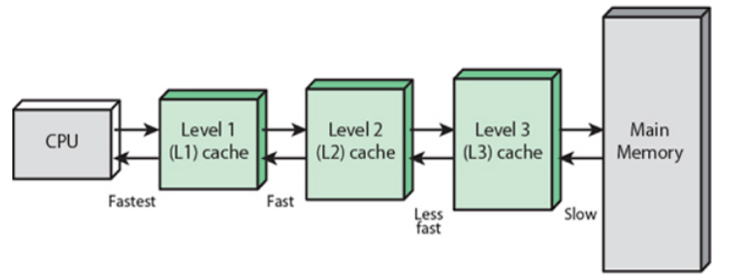
Figure: Cache Memory between CPU and Main Memory
Why cache is needed?
The cache memory is required to balance the speed mismatch between the main memory and the CPU. The clock of the processor is very fast, while the main memory access time is comparatively slower. Hence, the processing speed depends more on the speed of the main memory.
How cache memory is different from RAM?
Cache memory is a type of super-fast RAM which is designed to make a computer or device run more efficiently. By itself, this may not be particularly useful, but cache memory plays a key role in computing when used with other parts of memory.
Types of Cache Memory
There are multiple different kinds of cache memory levels as follows,
1. Level 1 (L1) or Registers
It is a type of memory in which data is stored and accepted that are immediately stored in the CPU. Generally, the L1 cache is the smallest in size and built into the processor chip. In multi-core CPUs, a separate L1 cache is available for each core.
Examples of L1 cache are accumulator, Program counter and address register, etc.
2. Level 2 (L2) cache or Secondary Cache
There are also L2 caches for larger processors but take longer to access. It is generally part of the CPU, but often a separate chip between the CPU and the RAM.
L2 is a secondary type of cache memory. L2 cache has more capacity than L1. It is located on a computer microprocessor.
The processor searches Instructions in the L1 cache, if required data or instructions not found then it searched into L2 cache. The high-speed system bus interconnecting the cache to the microprocessor.
3. Level 3 (L3) or Main Memory
The L3 cache is slower than L1 and L2 but larger. In Multi-core processors, each core may have separate L1 and L2, but all cores share a common L3 cache. L3 cache has double speed than the RAM.
It is a memory on which computer works currently. It is small in size and once power is off data no longer stays in this memory.
4. Level 4 (L4) or Secondary Memory
L4 cache is currently uncommon and is external memory which is not as fast as the main memory. Data retains permanently in this memory and is generally on (a form of) DRAM, rather than on static random-access memory (SRAM), on a separate die or chip (exceptionally, the form, eDRAM is used for all levels of cache.
Advantages of Cache Memory
The following are the advantages of cache memory:
- The main memory is slower than cache memory.
- It creates a way for fast data transfers so it consumes less access time as compared to main memory.
- It stores frequently access that can be executed within a short period of time.
Disadvantages of Cache Memory
The following are the disadvantages of cache memory:
- It is limited capacity memory.
- It is very expensive as compared to Memory (random access memory (RAM)) and Hard Disk.
References
Advertisement
Advertisement