Home »
Embedded Systems
AVR Microcontroller: What It Is, Architecture, and Types
In this tutorial, we will learn about the AVR (Virtual RISC, AVR), its architecture, and types.
By Suryaveer Singh Last updated : May 12, 2023
What is AVR Microcontroller?
AVR is the family of microcontroller which was developed by the ATMEL in the year 1996. These are the modified Harvard Architecture 8-bit RISC Single Microcontroller Chip. AVR stand for "Advanced Virtual Risc".
Architecture of AVR Microcontroller
AVR is the family of microcontrollers that was developed by the ATMEL in the year 1996. These are the modified Harvard Architecture 8-bit RISC Single Microcontroller Chip.
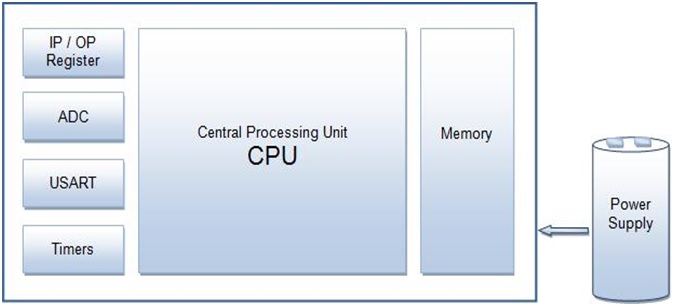
The above diagram above shows the basic architecture of the AVR. Where,
- ADC: Analog to Digital Conversion
- USART: Universal Synchronous Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter
- TIMERS: Provides delay to the microcontroller
AVR is one of the first Microcontrollers that uses on-chip flash memory for program storage. The first Microcontroller based on AVR architecture was AT90S8515.
Types of AVR Microcontrollers
There are three main types of AVR microcontrollers: TinyAVR, MegaAVR, and XmegaAVR. Let's discuss them.
- TinyAVR
Less memory, small size and suitable only for simpler applications.
- MegaAVR
These are the most popular ones, they have good amount of memory (upto 256 KB), higher number of inbuilt peripherals and is suitable for moderate to complex applications.
- XmegaAVR
It is mostly used commercially for complex applications, which require large program memory and high speed.
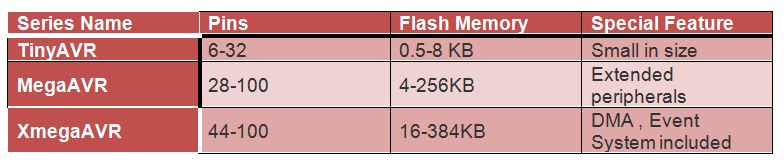
The program instructions in the AVR are stored in a non-volatile flash memory. The size of the program memory is indicated in the naming of the device itself. Example the ATmega64x line has 64 kb of flash and the ATmega16 has a 16 kb of a flash memory.
References
Advertisement
Advertisement