Home »
Data Structure
Depth First Search (DFS) of a Graph
In this article, we are going to see graph traversal method (DFS) with C++ implementation.
Submitted by Souvik Saha, on March 19, 2019
What you will learn?
How to implement Depth first search of a graph?
Depth First Search is a depthwise vertex traversal process. Like a tree all the graphs have vertex but graphs have cycle so in searching to avoid the coming of the same vertex we prefer DFS.
Algorithm:
To implement the DFS we use stack and array data structure.
There are two cases in the algorithm:
- Whenever we visit a vertex we mark it visited and push its adjacent non-visited vertices into the stack and pop the current vertex from the stack.
- If all the adjacent vertices are visited then only pop the current vertex from the stack.
Consider this graph,
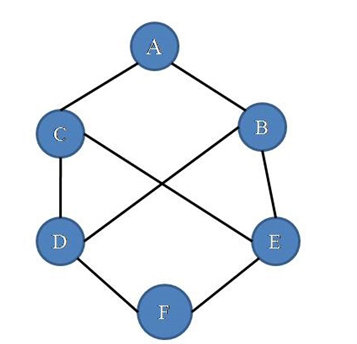
Our algorithm performs like following for the above graph:
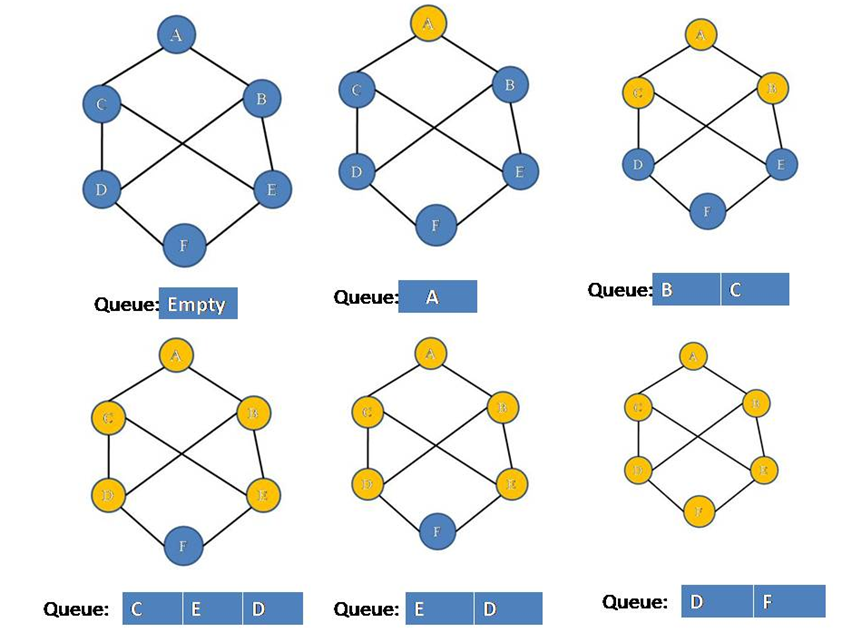
Hence all the vertices are visited then only pop operation is performed and stack will be empty at last.
C++ Implementation:
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
void addedge(list<int>,int ,int );
void DFS(list<int>*,int);
// Make a pair between vertex x and vertex y
void addedge(list<int> *ls,int x,int y){
ls[x].push_back(y);
ls[y].push_back(x);
return;
}
//Depth First Search of a Graph
void DFS(list<int>*ls,int num,int x){
bool *visit= new bool[num];
for(int i=0;i<num;i++){
visit[i]=false;
}
stack<int> st;
st.push(x);
while(!st.empty()){
int s=st.top();
st.pop();
if(!visit[s]){
cout<<s<< " ";
visit[s]=true;
list<int>::iterator it;
for(it=ls[s].begin();it!=ls[s].end();it++){
st.push(*it);
}
}
}
}
// Print the Adjacency List
void print(list<int> *ls,int num){
list<int>::iterator it;
for(int i=0;i<6;i++){
cout<<i<<"-->";
for(it=ls[i].begin();it!=ls[i].end();it++){
cout<<*it<<"-->";
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
int main(){
int num=6;
cout<<"Enter the no. of vertices : 6\n";
list<int> *ls=new list<int>[num];
addedge(ls,0,2);
addedge(ls,2,3);
addedge(ls,3,4);
addedge(ls,4,5);
addedge(ls,2,5);
addedge(ls,1,4);
addedge(ls,3,0);
cout<<"Print of adjacency matrix:"<<endl;
print(ls,6);
cout<<"DFS"<<endl;
DFS(ls,6,0);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter the no. of vertices : 6
Print the Adjacency List
0-->2-->3
1-->4
2-->0-->3-->5
3-->2-->4-->0
4-->3-->5-->1
5-->4-->2
DFS:
0 3 4 1 5 2
Advertisement
Advertisement