Home »
Data Structure
Traversal technique for Binary Tree
Learn: In this article, we will learn about Traversal technique for Binary tree with their algorithms and example.
Submitted by Abhishek Kataria, on June 11, 2018
Binary Tree
A binary tree is a finite collection of elements or it can be said it is made up of nodes. Where each node contains the left pointer, right pointer, and a data element. The root pointer points to the topmost node in the tree. When the binary tree is not empty, so it will have a root element and the remaining elements are partitioned into two binary trees which are called the left pointer and right pointer of a tree.
Traversing in the Binary Tree
Tree traversal is the process of visiting each node in the tree exactly once. Visiting each node in a graph should be done in a systematic manner. If search result in a visit to all the vertices, it is called a traversal. There are basically three traversal techniques for a binary tree that are,
- Preorder traversal
- Inorder traversal
- Postorder traversal
1) Preorder traversal
To traverse a binary tree in preorder, following operations are carried out:
- Visit the root.
- Traverse the left sub tree of root.
- Traverse the right sub tree of root.
Note: Preorder traversal is also known as NLR traversal.
Algorithm:
Algorithm preorder(t)
/*t is a binary tree. Each node of t has three fields:
lchild, data, and rchild.*/
{
If t! =0 then
{
Visit(t);
Preorder(t->lchild);
Preorder(t->rchild);
}
}
Example: Let us consider the given binary tree,
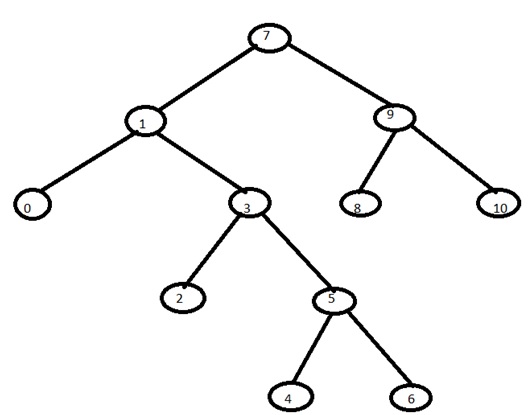
Therefore, the preorder traversal of the above tree will be: 7,1,0,3,2,5,4,6,9,8,10
2) Inorder traversal
To traverse a binary tree in inorder traversal, following operations are carried out:
- Traverse the left most sub tree.
- Visit the root.
- Traverse the right most sub tree.
Note: Inorder traversal is also known as LNR traversal.
Algorithm:
Algorithm inorder(t)
/*t is a binary tree. Each node of t has three fields:
lchild, data, and rchild.*/
{
If t! =0 then
{
Inorder(t->lchild);
Visit(t);
Inorder(t->rchild);
}
}
Example: Let us consider a given binary tree.
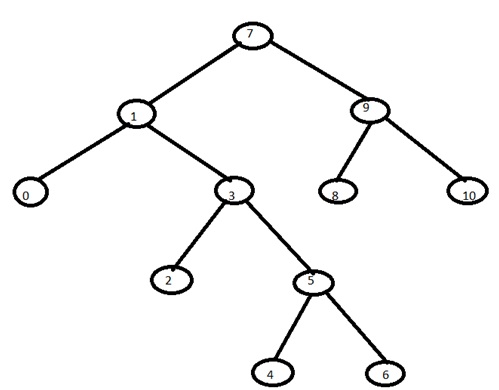
Therefore the inorder traversal of above tree will be: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10
3) Postorder traversal
To traverse a binary tree in postorder traversal, following operations are carried out:
- Traverse the left sub tree of root.
- Traverse the right sub tree of root.
- Visit the root.
Note: Postorder traversal is also known as LRN traversal.
Algorithm:
Algorithm postorder(t)
/*t is a binary tree .Each node of t has three fields:
lchild, data, and rchild.*/
{
If t! =0 then
{
Postorder(t->lchild);
Postorder(t->rchild);
Visit(t);
}
}
Example: Let us consider a given binary tree.
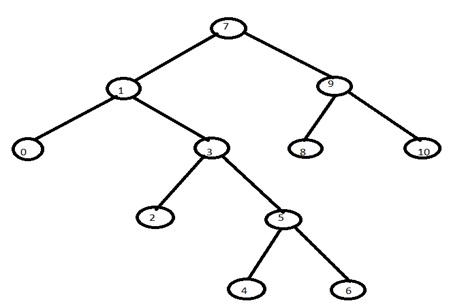
Therefore the postorder traversal of the above tree will be: 0,2,4,6,5,3,1,8,10,9,7
Advertisement
Advertisement