Home »
Data Structure
Sum of all left leaf nodes in a given tree
In this article, we are going to see how to find the sum of all left leaf nodes in a given tree?
Submitted by Radib Kar, on August 27, 2020
Prerequisite: Sum of all right leaf nodes in a given tree
Left leaf node means which is a leaf node and also left child of the parent. So, to do this we can use any of the traversal techniques we have learnt already. We can either use depth-first based traversal (inorder/preorder/postorder), or breadth-first based traversal (level order traversal). While traversing what we need is to keep checking whether the current node has any left child which is a leaf node too. If the node has then we add the left child node value with the cumulative sum.
In the below example,
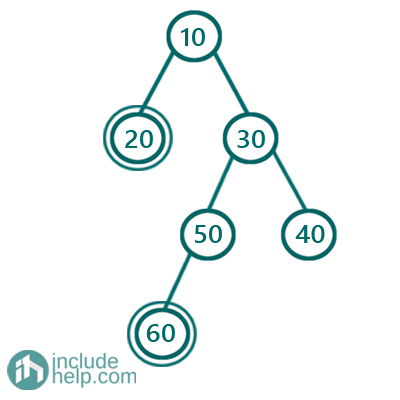
We can see that the left leaf nodes are 20 & 60, so the sum will be 80.
But in the below example,
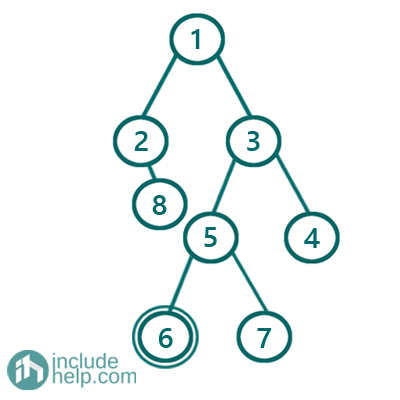
The only left leaf node is 6 and thus sum would be: 6
Solution:
1) Using depth-first based traversals:
Here I have used inorder traversal to traverse the tree. The solution is pretty much the same as we did in Sum of all right leaf nodes in a given tree. But, here the constraint is different and now the constraint is we need to sum up leaf nodes which are a left child of its parent node. Below is the detailed implementation.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// tree node is defined
class TreeNode {
public:
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int data)
{
val = data;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
//depth first traversal and summing
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int& sum)
{
if (!root)
return;
//if it has left child and the child is leaf node
//then add the child value
if (root->left && !root->left->left && !root->left->right)
sum += root->left->val;
dfs(root->left, sum);
dfs(root->right, sum);
}
int leftLeafSum(TreeNode* root)
{
//Code here
int sum = 0;
dfs(root, sum);
return sum;
}
int main()
{
//building the tree like example1
TreeNode* root1 = new TreeNode(10);
root1->left = new TreeNode(20);
root1->right = new TreeNode(30);
root1->right->left = new TreeNode(50);
root1->right->right = new TreeNode(40);
root1->right->left->left = new TreeNode(60);
cout << "Sum of all left leaves in the Example1 is: " << leftLeafSum(root1) << endl;
//building the tree like example2
TreeNode* root2 = new TreeNode(1);
root2->left = new TreeNode(2);
root2->right = new TreeNode(3);
root2->left->right = new TreeNode(8);
root2->right->left = new TreeNode(5);
root2->right->right = new TreeNode(4);
root2->right->left->left = new TreeNode(6);
root2->right->left->right = new TreeNode(7);
cout << "Sum of all left leaves in the Example2 is: " << leftLeafSum(root2) << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
Sum of all left leaves in the Example1 is: 80
Sum of all left leaves in the Example2 is: 6
2) Using breadth-first traversal:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// tree node is defined
class TreeNode {
public:
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int data)
{
val = data;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
//breadth first traversal and summing
void bfs(TreeNode* root, int& sum)
{
if (!root)
return;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
//do a level order traversal and keep adding node values
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* temp = q.front();
q.pop();
//if it has left child and the child is leaf node
//then add the child value
if (temp->left && !temp->left->left && !temp->left->right)
sum += temp->left->val;
if (temp->left) {
q.push(temp->left);
}
if (temp->right)
q.push(temp->right);
}
}
int leftLeafSum(TreeNode* root)
{
//Code here
int sum = 0;
bfs(root, sum);
return sum;
}
int main()
{
//building the tree like example1
TreeNode* root1 = new TreeNode(10);
root1->left = new TreeNode(20);
root1->right = new TreeNode(30);
root1->right->left = new TreeNode(50);
root1->right->right = new TreeNode(40);
root1->right->left->left = new TreeNode(60);
cout << "Sum of all left leaves in the Example1 is: " << leftLeafSum(root1) << endl;
//building the tree like example2
TreeNode* root2 = new TreeNode(1);
root2->left = new TreeNode(2);
root2->right = new TreeNode(3);
root2->left->right = new TreeNode(8);
root2->right->left = new TreeNode(5);
root2->right->right = new TreeNode(4);
root2->right->left->left = new TreeNode(6);
root2->right->left->right = new TreeNode(7);
cout << "Sum of all left leaves in the Example2 is: " << leftLeafSum(root2) << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
Sum of all left leaves in the Example1 is: 80
Sum of all left leaves in the Example2 is: 6
Advertisement
Advertisement