Home »
Interview coding problems/challenges
Ancestors in Binary Tree
Ancestors in Binary Tree: In this article, we are going to see how to find ancestors for a node in binary tree?
Submitted by Radib Kar, on March 25, 2019
Problem statement
Given a Binary Tree and a target key, write a function that prints all the ancestors of the key in the given binary tree.
Example:
Let's the tree be like following:
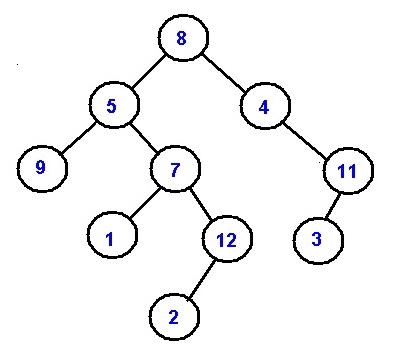
Let for node value 12:
Ancestors are:
7, 5, 8
While for node value 7:
Ancestors are:
5, 8
Solution
What is Ancestors?
For any node n,
Its ancestors are the nodes which are on the path between roots to node n
Thus for the above examples,
Example 1:
Node is 12 //represented by value
Root to the node path is
8->5->7->12
Thus the ancestors are 7, 5, 8
Example 2:
Node is 7 //represented by value
Root to the node path is
8->5->7
Thus the ancestors are 5, 8
Algorithm:
FUNCTION printAncestors(Node *root, int target)
IF(!root)
return false;
IF( (root->left && root->left->data==target) ||
(root->right && root->right->data==target ) ||
printAncestors(root->left,target)||
printAncestors(root->right,target)){
Print root->data;
return true;
END IF
return false;
END FUNCTION
That simply means we are doing kind of DFS
For a currentnode to be ancestor of the target node the conditions are:
1. If the target node is its child node (either left child or right child)
//condition
IF((root->left && root->left->data==target) ||
(root->right && root->right->data==target ))
2. If any of the two subtree of the current node contain ancestor of the target
node then the current node is also an ancestor.
//condition
IF(printAncestors(root->left, target)||
printAncestors(root->right, target))
Example with explanation:
For target node 7:
Root 8 is ancestor on condition: its left subtree contains ancestor 5
5 is ancestor since target node is its right child
Thus ancestors are:
5, 8 //in order
C++ Implementation
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//tree node
class Node{
public:
int data;
Node *left;
Node *right;
};
bool printAncestors(Node *root, int target)
{
if(!root)
return false;
if( (root->left && root->left->data==target) ||
(root->right && root->right->data==target ) ||
printAncestors(root->left,target)||
printAncestors(root->right,target)){
cout<<root->data<<" ";
return true;
}
return false;
}
//creating new nodes
Node* newnode(int data){
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return(node);
}
int main() {
//**same tree is builted as shown in example**
cout<<"tree in the example is build here"<<endl;
//building the tree like as in the example
Node *root=newnode(8);
root->left= newnode(5);
root->right= newnode(4);
root->right->right=newnode(11);
root->right->right->left=newnode(3);
root->left->left=newnode(9);
root->left->right=newnode(7);
root->left->right->left=newnode(1);
root->left->right->right=newnode(12);
root->left->right->right->left=newnode(2);
int s;
cout<<"enter input value to find ancestors......"<<endl;
cin>>s;
printAncestors(root,s);
return 0;
}
Output
tree in the example is build here
enter input value to find ancestors......
7
5 8
Advertisement
Advertisement