Home »
Software Engineering
Classical Waterfall Model in SDLC
In this tutorial, we will learn about the Classical Waterfall Model in Software Life Cycle Model (SDLC).
By Monika Sharma Last updated : April 05, 2023
What is Classical Waterfall Model in SDLC?
The Classical Waterfall Model is one of the oldest software lifecycle models that were developed to provide a systematic approach to the developers for developing any software. It can be said that all the other software lifecycle models were derived from this classical waterfall model just by adding some additional features and omitting some.
The name waterfall itself defines the characteristics of the model. As a waterfall flows only downwards and cannot flow back, in the same way, the phases in the waterfall model are followed one after the other in the same sequence as mentioned. And after completing a phase and entering into another phase, we cannot go back to the previous phase.
Classical Waterfall Model Phases
The different phases that are included in Classical Waterfall Model in Software Life Cycle Model (SDLC) are:
- Feasibility study
- Requirement analysis and specification
- Design
- Coding and unit testing
- Integration and system testing
- Maintenance
An overview of these phases of Classical Waterfall Model in Software Life Cycle Model (SDLC) can be made from the following diagram:
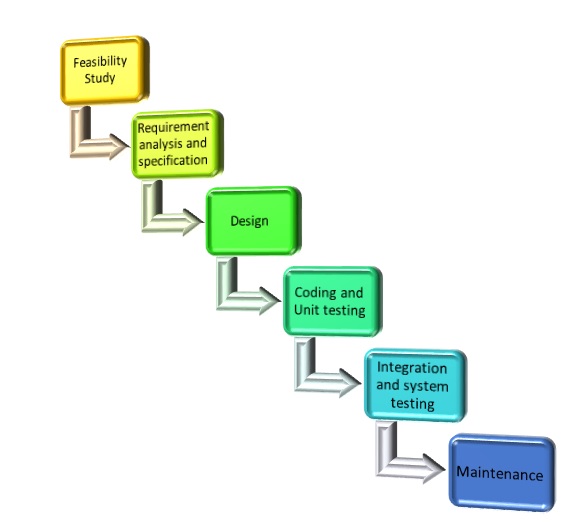
Different Phases of Classical Waterfall Model
The different processes that are followed in each of these phases while the entire software development process:
1) Feasibility study
In the feasibility study, we try to study the software in terms of technical and business aspects, to determine whether it would be beneficial for the company (or the organization) to build the particular software, whether the consumers will be satisfied through it or not and how much profit the software will be able to provide us.
The feasibility study takes place as follows:
- A rough understanding of the project by the team leaders and heads from the client-side.
- Analyzing every aspect of the client's views and reaching a state overall understanding of the project is made.
- Picking up the best solution.
2) Analysis and specification
Here, all the requirements of the software are analyzed and documented properly. This is a very important phase because, in the classical waterfall model, each requirement must be documented in this phase itself because we cannot add or modify any of them in the later phases of development. This phase mainly involves two things:
- Requirements gathering
- Requirements specification
3) Design
In the design phase, a blueprint of the entire software is created. How the software must appear as a final product is decided in the designing phase itself. Hence, the design of the software gives an overview of the software to the developers so that they can work on that accordingly. This is done so that all the requirements are transformed into a structural manner which now makes it easier for the developers to implement.
The designing team can follow different approaches like the traditional approach, the procedural approach, the object-oriented approach, etc.
4) Coding and unit testing
In the coding phase, the developers code the program in any suitable programming language. While developing any feature of the software, the developers also have to test the feature on their level to check whether it is working fine or not. Therefore, the testing involved in this phase is termed as unit testing.
5) Integration and system testing
Different developers work on different subprograms. Now, all these subprograms need to be integrated to get our final software. Also, when the subprograms (or modules) are integrated, then they may function in a different manner which is not expected. SO, it is the job of the tester now to check the software for each functionality. There are three testing rounds that software must undergo before the deployment of the final software. They are:
- Alpha testing
- Beta testing
- Acceptance testing
6) Maintenance
After the final testing, the software may require some maintenance before getting deployed. Even after getting deployed, there can occur certain problems that may occur in the software with the use. All these are also handled and maintained in the maintenance phase of the software lifecycle.
Each of the phases of this model is executed one after the other. You cannot break the flow and you cannot go back to the previous phase as stated earlier.
This means that if you are in the design phase, then you cannot conduct the requirement analysis and specification study for the software. That has already been earlier and now there is no scope left for making any kind of changes in the software requirements according to Classical Waterfall Model in Software Life Cycle Model (SDLC). All that needs to be completed before getting onto the design phase.
We can also relate this model with our many days to day activities that must be performed in a particular order. This can be well understood with the following example:
Suppose you want to make a dish in a couple of hours. Then your feasibility phase and requirement analysis phase starts in the initial phase of making the dish itself. First, you need to decide what you will be making. That is your feasibility study. Now let’s say your requirements include chopping board, vegetables, flour, spices, oil, etc. You need to list them up before going to the market itself. That’s your requirements and specification phase. Now you prepare everything up and assemble in the utensil. That’s the designing part. And the cooking and tasting part becomes your coding and testing part. Final plating of the dish in the integration part and then you finally present your dish in front of the customers. After that, adding any sort of extra spices or re-heating the dish in some cases can be thought as of your maintenance part.
So you see, if you skip any of the phase-in between or break the flow of these phases, then you will not be able to present your final dish in front of the customers on time.
Advertisement
Advertisement