Home »
Management Information System
Framework for MIS Organization and Management
In this tutorial, we will learn about the Framework for MIS Organization and Management.
By IncludeHelp Last updated : June 01, 2023
Robert Anthony from the University of Chicago; in the year 1965 proposed a framework for the MIS system which mainly consists of three components. These components are Strategic Planning, Operational Control, and Management Control. The following figure is describing its basic structure and the connectivity of its key components –
Strategic Planning
Strategic planning is a method of focusing on improvements in the goals of the organization, the methods that are to be used to achieve these objectives; policies that are frame by management experts to control, organize, and use organizational resources to reduce the cost and maximize profit. Overall, strategic planning helps in designing the strategies of the company, and is used in formulating policies to control the acquisition, handling of the business activities, and gets involved in reframe strategy whenever required. From a philosophical perspective, strategic planning must be design in such a way so that an organization may achieve its aim and objectives as well as can keep itself up to date on new developments through changes to the objectives, the financial aspects of the resources needed, and the guiding principles and policies to be followed in obtaining, using the organizational resources.
Operational Control
Operational control is a process of managing operational activities of an organization that are carried out to achieve optimal utilization of the resources and successful implementation of the operational activities in an organization like production, production, stock management, financial process, HRM, etc. To run it smoothly, matrices allow for pre-established processes and decision rules to be used, the constant assurance of effective acquisition and use of resources in the areas in which the results can be reasonably well understood, and operations are optimally organized and managed. For an instance – the directives set by our superiors are followed as per our ability and that the tasks we perform effectively and efficiently. These decisions at lower levels of the company have very little effect on the organization. There is a fixed timeline for decisions being taken, and there are certain "routines" that immediately proceed to complete the process.
Management Control
Management control is a process of assuring that resources are collected and used effectively and efficiently, resulting in the accomplishment of the organizational key objectives. In this process, an executive or superiors, or managers will use to assess the productivity of his/her department, identify the issues, formulate some new and innovative strategies, make some rules of control, set protocol, and evaluate the risk allocation of resources. This job is mainly taking care of the middle-level management of the company. At this level, managers must be taking advice from the strategic planning hierarchy and must be monitoring the organization's activities so that the strategic priorities can be set and accomplished efficiently and successfully.
Relationship between Operations, Planning and Control
The details given by an MIS helps the managers to make decisions that are not involved. An organization must conduct certain activities to prevent itself from running into serious causes. For example “in a production of any product, a common process has to perform certain production activities" like a wholesaler has to obtain and dispatch goods, a municipal corporation has to provide water supply to its area of jurisdiction. In addition to its day-to-day activities, a company must also prepare for its potential closing operations. To predict trends, the company has to make a prompt decision about how much production of a particular product needs to make for the upcoming time.
In an organization, the planning process and goals set out at the time of the planning process decides the scope of the organization’s operations. During the production process, it has to know whether a decision has to be taken to make corrections or revise on pre plans based on the tests. Interestingly, all that the wholesaler would do is correct the deviation or update the plans. It might be important to control organizational activities with effects to ensure companies' existence in the market. The following figure is illustrating the same -
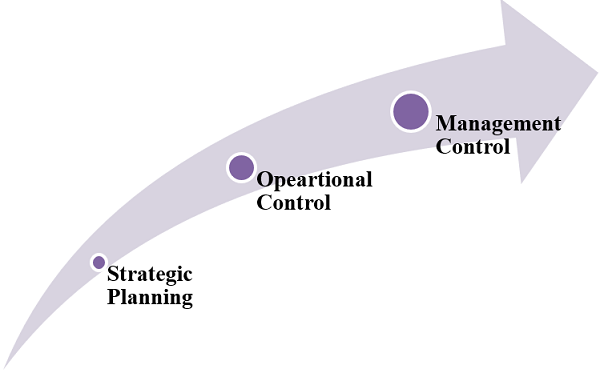
MIS is one that is concerned with planning and control. When running, we can benefit from having several systems for obtaining information. For example, the carmaker would have sensors installed in the car, programming a system on the shop floor for giving the workers their information about the task that is required on a specific batch of material. Along with the rate materials being pushed along route sheets, other materials are moving at different rates at any given moment. This system by itself contains only the necessary information to support operations. It does not have any high-level decision-making meaning. It is not part of his/her medical record. If, however, the system does include information on efficiency, computer utilization, or rejection rates (anything which is relevant to business or productivity), then we can conclude that the system is a part of an MIS.
The levels of management
Organizations have several levels, each of which offers a different context. This could be categorized into several categories; multiple- categories of the levels (Senior, middle and lower).
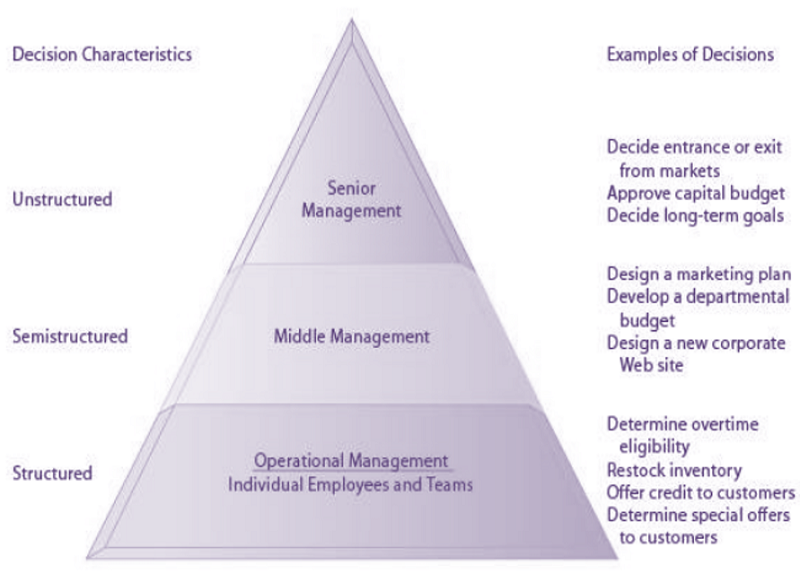
This organization is ruled by the top management, and they conduct strategic planning and the two lower levels provide processing of the information for their work. The middle management level is responsible for preparing the tactical management strategies and controls and needs to get information to execute the level. The junior level of the company is involved in day-to-day operational management, and they need knowledge for their working to be effective.
- Decisions are being taken at all levels of the business.
- Now and then, making an extraordinary and rare decision will change everyone's future.
- Change IT offers new tools for managers to carry out business decisions.
- Receive the most concrete, up-to-date information and relay it as quickly as possible to those who need to be aware of it.
It does not provide some information explicitly but offers some capabilities to the user to evaluate the decision-making problem and produce some significant information, which can be used as a data sample of the decision problem.
Advertisement
Advertisement