Home »
Management Information System
Rapid Application Development (RAD) Model in Management Information System
SDLC RAD Model in MIS: In this tutorial, we will learn about the SDLC Rapid Application Development (RAD) Model in Management Information System, its phases, advantages, and disadvantages.
By IncludeHelp Last updated : June 01, 2023
What is Rapid Application Development (RAD) Model?
RAD stands for "Rapid Application Development"; this model is used to develop a system rapidly. In this model, overall project tasks divided into more than one team. Each team works to develop the system according to SDLC phases. When a system needs to develop in a very short time then the RAD model is the most suitable option amongst available SDLC models.
Phases of RAD Model
Followings are the phases of the RAD model,
- Business Modeling
- Data Modeling
- Process Modeling
- Application generation
- Testing and turnover
The initial task starts with communication between expert developers and customers. Planning is one of the most important criteria, after planning the overall process divides into classes. More essential is planning to work together on various project activities.
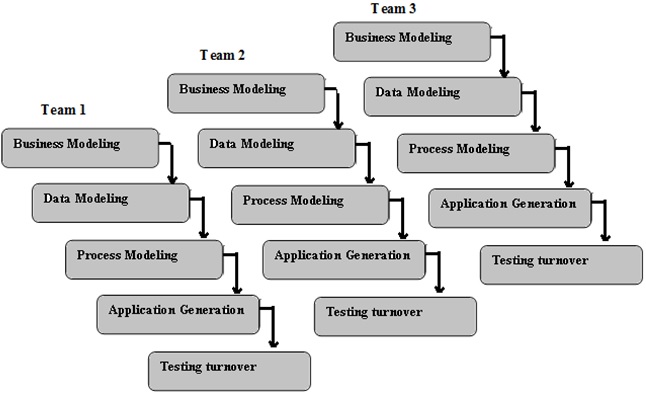
Figure: RAD Model
1) Business Modeling
Business analysis is required to obtain the necessary business information. Business Modeling is the transfer of knowledge between different roles within the enterprise. For example, what type of information each function generates, and what are the functions for handling that information.
2) Data Modeling
The knowledge is distilled into the collection of objects in the business modeling process and is important for the business. That object's attributes are established and the relation between the objects is defined.
3) Process Modeling
To enforce the business model, the data objects identified in the data modeling process are modified to fulfill the information flow. The definition of the process is created to add, modify, remove or retrieve a data object.
4) Application Generation
The actual framework is designed up during the application generation process. The automated system is used to build the framework.
5) Testing and Turnover
After each iteration, the designs are evaluated separately so that the total testing period is reduced. The data flow between all the components and the interfaces are thoroughly checked. Hence, most components of the programming are already being evaluated.
Advantages of RAD Model
- This model raises application development at a high pace.
- Due to parallel processing, delivery processes are fast.
- This model is flexible when modifications are required.
Disadvantages of RAD Model
- This model is not suitable for long-term projects or big ones.
- User input at each development step is expected.
Advertisement
Advertisement